© 2010-



Dielectric permittivity and conductivity of hydrogen at isentropic compression up to 3 Mbar
Extreme state of matter
An evolution density of states in argon with xenon admixture and in pure argon under
ultra-

Theory of strongly correlated Fermi-
A variation theory of the strongly correlated state is a generalization of the Gutzwiller’s
theory (closest neighbors are included). This theory allowed investigating the short-
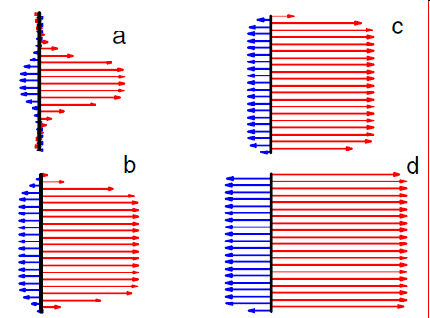
Calculated magnetic structure of the superlattice [Fe(2)/V(12)/Fe(3)V(12)]20 at different temperatures. Red and blue color show Fe(3) and Fe(2) layers magnetization.
Magnetoelectric effect on palladium surface and in the structure Pd/BaO/Pd
A magnetoelectric effect is the magnetization change under the external electric
field. It could be used for stimulation of a ferromagnetic (FM) state of a surface
layer of almost ferromagnetic metal. In the theory of itinerant magnetism a transition
of a paramagnetic metal to the FM phase is determined by the Stoner criterion. Palladium
is a well-
Below one can see a supercell and DOS of the calculated structure (the dotted line shows a shift of the Fermi level)
Solid state physics and nanosystems
The Laboratory develops different theoretical models of electronic structure of strongly
correlated and magnetic systems, and also the first-
Frustrated and low-
There are several well-
Other results of 2D simulation of magnetization dynamics are presented here (files in AVI format):
- at temperature T=10K at the magnetic field rise time of 0.1 T/min
- at temperature T = 5 K at the magnetic field rise time of 0.01 T/min
- at temperature T = 10 K at the magnetic field rise time of 0.01 T/min
3D simulation of of magnetization dynamics (file in AVI format):at temperature T=8K at the magnetic field rise time of 0.1 T/min (average magnetizations of chains are shown in color, magnetic moments arrangements in slices are shown at the bottom)
Nanosystems
Kondo-
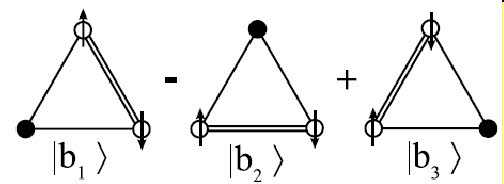
Structure of the ground state of the equilateral chromium trimer bound with a gold surface


Below one can see an evolution of the magnetic structure Ca3Co2O6 in 2D model at temperature T=5K at the magnetic field sweep rate of 0.1 T/min. Black and white show directions of the magnetization chains. Formation of a domain structure is seen.




